

Reconstruction suffered from poor leadership and uncertainty of direction, but it also laid the groundwork for renewed struggles for racial equality during the Civil Rights Movement. But the failures cannot obscure a number of notable accomplishments, with decisive long-term consequences for American life: the 14th and 15th Amendments to the Constitution, the election of the first African American representatives to the US Congress, and the avoidance of any renewed outbreak of civil war. Reconstruction also struggled to successfully manage the Southern resistance towards a Northern, free-labor pattern. Among its chief failures was the inability to chart a progressive course for race relations after the abolition of slavery and rise of Jim Crow. It succeeded in reuniting the nation politically after the Civil War but in little else. The era known as Reconstruction is one of the unhappiest times in American history. Oxford Research Encyclopedias: Global Public Health.The European Society of Cardiology Series.Oxford Commentaries on International Law.In both instances, the Federal government was viewed as a ‘reluctant ally’ of the blacks and their progressive white supporters, whereas the opponents to black equality were primarily white Southern Democrats and substantial numbers of white small-business and working-class people. Both were fought primarily in the Southern US, although in certain respects both inspired major socio-economic reforms in the Northern states as well. Both elevated articulate and charismatic black leaders from the Afro-American working class and fragile middle class. Both movements brought about the end of rigid racial/caste structures which had been used to oppress blacks for many decades.

Indians, Chicanos, Puerto Ricans, Asians) in the nation’s economic, social and political institutions. Like the former period, the Second Reconstruction was a series of massive confrontations concerning the status of the Afro-American and other national minorities (e.g.

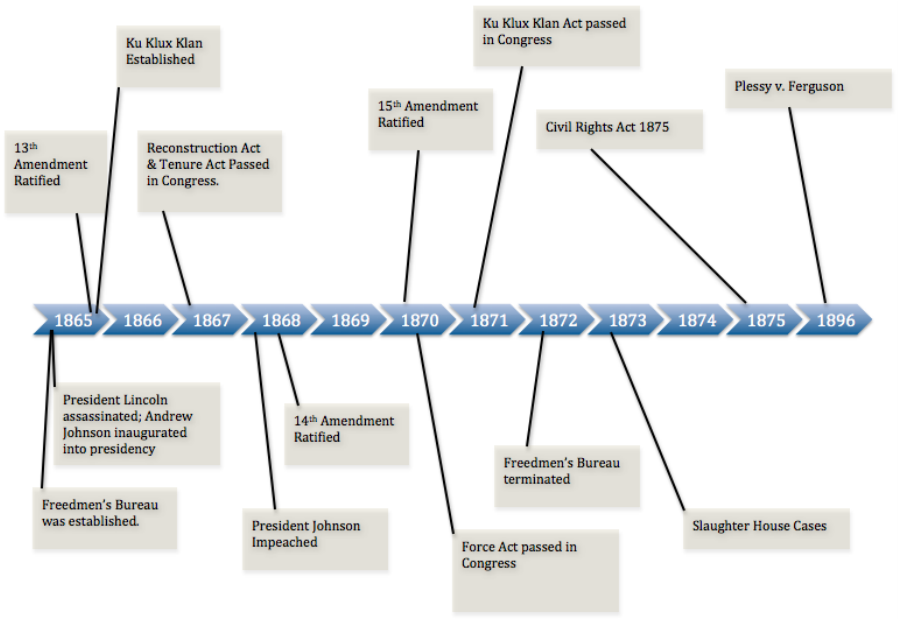
Almost a century later, a ‘Second Reconstruction’ occurred. The first was developed before the seminal conflict in American history, the Civil War (1861–65), and came to fruition in the twelve-year period of reunion, reconstruction and racial readjustment which followed (1865–77). During two brief moments in history, the United States experienced major social movements which, at their core, expressed a powerful vision of multicultural democracy and human equality.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
